Gulf of Alaska: Two Oceans Meet, But Do Not Mix
Last Updated on 29th September 2025 by admin
The Gulf of Alaska is in the northeastern Pacific Ocean, off the southern coast of Alaska, between the Alaska Peninsula and the Alexander Archipelago.
Table of Contents
About Gulf of Alaska
Gulf of Alaska refers to an arm of the Pacific Ocean and occupies about 592,000 square kilometers (228,000 square miles). The gulf is surrounded by scenic and rocky landscapes that draw tourists worldwide and one of the USA’s attractions. The Gulf of Alaska is a rich marine environment that hosts numerous fish species, such as salmon, halibut and cod. It also holds significant marine mammals like sea otters, seal and whales.
There are numerous weather conditions that affect the region such as strong winds, high seas, and frequent storms. The Gulf of Alaska is also an active seismic region and has several underwater volcanoes. It is an important economic and cultural asset to the local people of the area and commercial fishing and shipping sectors.

Gulf of Alaska’s Hidden Mysteries
Do you believe in magic? Well, there is a secret in the Gulf of Alaska that will leave you spellbound. Just imagine a place where two oceans meet, but don’t mix! This is one such mysterious location that has puzzled scientists over the years.
The world is full of mysteries and there are some such things that can not be less than a miracle. 70% of our planet filled with water only. It is extremely challenging to locate the start and the finish of the oceans. We are now going to tell you about a weird thing in the Gulf of Alaska, which is in the northern Pacific Ocean and holds some of the secrets of the two oceans.
In the Gulf of Alaska there is a spot where the two oceans meet, but they do not mix their water, which we can distinguish clearly in their waters. It is very amazing when the electric blue water comes in contact, but does not blend with dark blue water
This meeting results in a visual effect where the waters are seen to be of two different colors and never mix completely. This article will discuss the science, the origin of the two distinct colors, and the importance of the natural phenomenon on the environment. This article is going to unlock the secrets behind the Gulf of Alaska, we are going to find out the facts about the two oceans meet but don’t mix their water.
Gulf of Alaska Facts
The gulf of Alaska is a wonder and a mystery, where two oceans come together without being mixed. This wonderful body of water has gripped the hearts and minds of people all over the world, and justifiably so. These are some of the interesting facts about the Gulf of Alaska that will make you awe struck.
The meeting point of two oceans:
The meeting point of two oceans in the Gulf of Alaska is a spectacular view that shocks people. The difference between the warm, blue Pacific Ocean waters and the milky turquoise Arctic Ocean waters is dramatic. It is the reminder of the greatness and the beauty of nature and we should do something to save this wonder against environmental threats. This is a beautiful natural phenomenon and we should make sure that it is a healthy ecosystem in the generations to come.
These two oceans appear as a line that can be seen from several kilometers away where the two oceans meet. The line is not always straight, and may move and vary with the weather and tides. In some cases, the two oceans may even blend because of the strong winds, waves, or currents.
The cause of the two different colors of water:
The Alaska Current waters are colder in temperature and rich in nutrients, which are brown or green in color since the water has suspended sediments, algae, and other forms of organic matter. These nutrients are also necessary to the growth of phytoplankton which supports the whole marine food chain. North Pacific Current has warmer and saltier waters that are blue or turquoise because there is no suspended matter and algae.
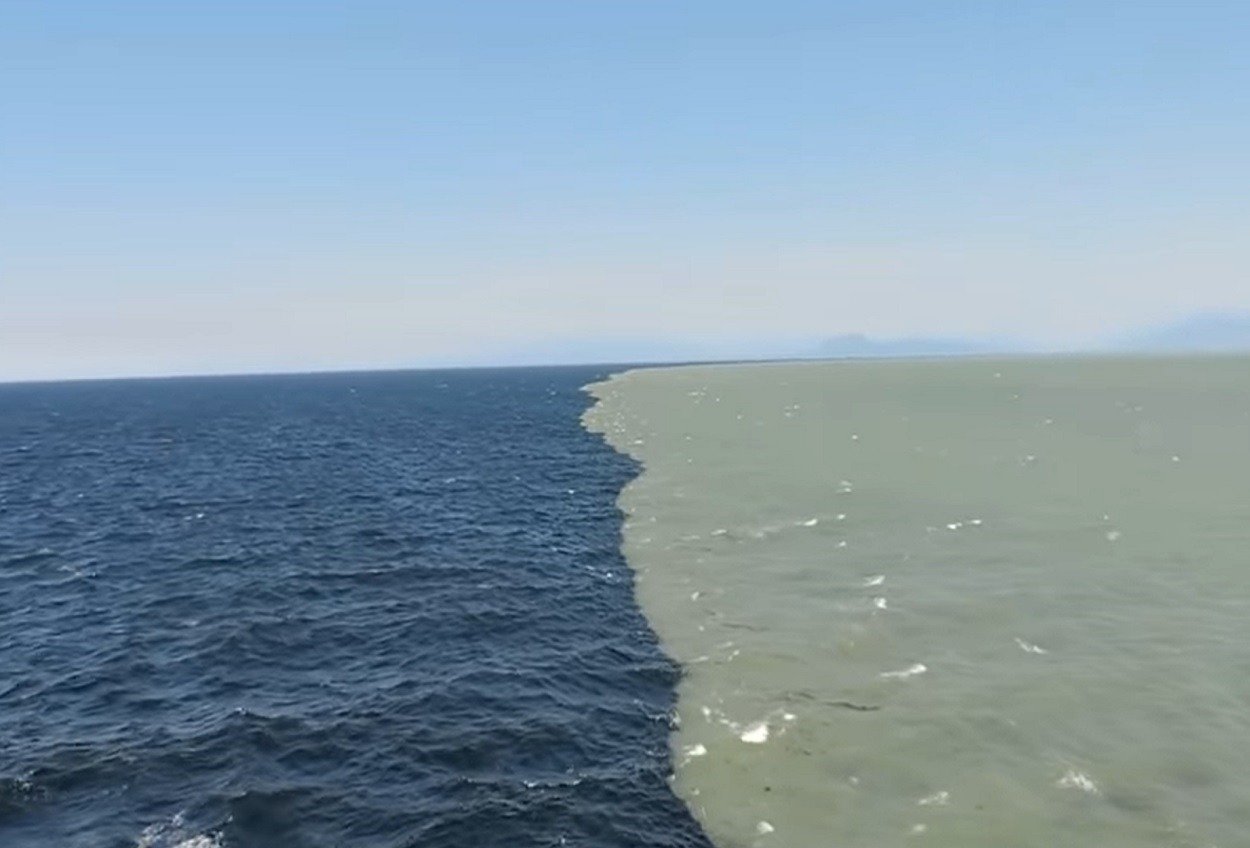

The meeting of the two currents causes the nutrients and sediments of the Alaska current to enter into the North Pacific current resulting in the brown or green color at the surface. At the same time, the blue or turquoise waters of the North Pacific Current are still visible beneath the surface. This gives a very strong visual image of the two contrasting colors of water that seem to be next to each other, though they are never completely blended.
The depth of the Gulf of Alaska:
The gulf of Alaska is very mysterious and awe-inspiring in depth. It has a depth of over 1500 meters on average, and a depth of more than 4000 meters on its highest point, which makes it one of the deepest bodies of water in the globe. The Gulf of Alaska is a very interesting place to explore, as it offers a rich range of marine life and geological features.
It is a reminder of the sheer strength of the ocean and the wonders that are beneath in the depths. However there are also challenges and risks in the depth of the Gulf of Alaska. Sailing in these deep and heavy waters involves skill and caution and extreme conditions may be hazardous to even the most experienced sailors. It is also complicated to study and learn the ecosystem of the this area due to depths.
The Climate of the Gulf of Alaska:
- “The climate of the Gulf of Alaska is mysterious as it is varied. The weather conditions of the region are ever changing, shifting between icy fjords and lush rainforests, thus making the landscapes awe-inspiring and unpredictable at the same time.”
- “Surviving the climate of the this area is not an easy feat. The tempestuous seas, the extreme weather patterns, remind the region of the great power of nature.”
- “The climate of the Gulf of Alaska is the contrast study, as the mountains with snow-caps are shortened by the forest and the enormous Pacific Ocean. However, the weather in the region is magnificent and tumultuous as astonishingly beautiful.”
- “The climate is something to reckon. The weather is unpredictable, like bitter cold winters, summer storms, which can rival hurricanes, the region can change at a moment it is not always an easy place to call home.”
- “The climate of the Gulf of Alaska is complicated as much as the geography of the area. A combination of Arctic and Pacific influences, the region has among the wildest weather patterns in the whole world, making its climate interesting and unpredictable.”
Gulf of Alaska Oceans – Why Don’t They Mix?
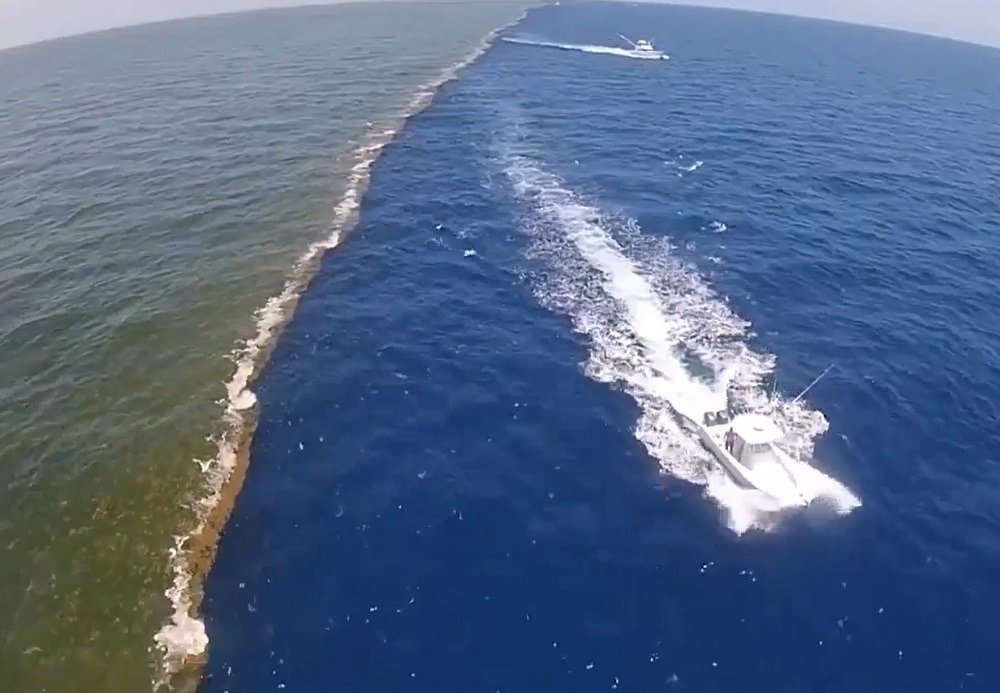
The view of the gulf of Alaska is one to envy. The gulf contains two different water colors, the one is blue and the other is green. The Pacific Ocean is the source of the blue water and the glacial melt going through the Copper River is the source of the green water. The contrast in color is an image that anyone who has seen it cannot forget.

Where Two Oceans Meet
The most extraordinary thing about the Gulf of Alaska is that two oceans meet, but do not mix. So, what is the science behind this unusual phenomenon? They are two worlds hitting each other, and yet preserving their respective identities. This effect of the two colors of water not mixing is called a “color line,” or a “color boundary. This phenomenon has been the focus of scientists over the years and they have developed a number of theories to explain it.
Theory 1 – Surface Tension:
The first theory is that the two oceans do not blend because of surface tension. The temperature and density disparity provides a barrier that does not allow the mixing of the water. The surface tension acts like a thin layer that keeps the two masses of water apart.
Theory 2 – Coriolis Effect:
The second theory is that the Coriolis Effect is the reason that makes the two oceans separate. The Coriolis Effect is what makes the fluids such as water move in a curved direction instead of a straight line. This effect is due to the rotation of the earth which may have led to the separation between the two oceans.
Theory 3 – Density Difference:
The third theory is that the separation of the two oceans is due to the difference in density. The Pacific Ocean is light and not as dense whereas the Arctic Ocean is cold and dense. This forms a barrier between the two masses of water making them not to mix.

The Environmental Significance:
The ecological and environmental implications of the unique oceanography of the Gulf of Alaska are great. The Alaska Current provides a rich support system of nutrient rich waters, as well as commercially significant fish species like salmon and halibut. There is also a significant marine mammal habitat that supports marine mammals like sea otters and humpback whales. But there are also other environmental threats like oil spills and global warming to the Gulf of Alaska.
The Gulf of Alaska oil spill has the potential to cause drastic impacts in the local ecosystem, especially the fisheries of salmon and herring. Also, the climate change is leading to alteration of ocean temperature and currents which may have unknowing impacts on the unique color line and ecosystem of the Gulf of Alaska.
In summary, the Gulf of Alaska is an excellent water resource that supports a variety of rich marine life. The meeting of the two oceans and the division has puzzled scientists over the years. It is not only a beautiful place, but it is also a distinct ecosystem, sustaining numerous species of fish, whales, seals, sea lions, and seabirds. It is our responsibility to preserve this miracle of nature’s natural wonder and make it a flourishing ecosystem to be enjoyed by successive generations.
FAQs
- What is the average temperature of the Gulf of Alaska?
The average temperature of the Gulf of Alaska ranges from 6-10°C.
- What is the largest city near the Gulf of Alaska?
Anchorage is the largest city near the Gulf of Alaska.
- What is the depth of the Gulf of Alaska?
The Gulf of Alaska is one of the deepest oceans in the world, with depths reaching up to 15,000 feet.
- What is the primary industry in the Gulf of Alaska?
The primary industry in the Gulf of Alaska is fishing.
- What is the best time to visit the Gulf of Alaska?
The best time to visit the Gulf of Alaska is during the summer months, from May to September, when the weather is milder and the wildlife is more active.